The sheer volume of applications, the growing size of users, the ever-expanding demand for technology, and the constant quest for real-time response. Consider whether this is exactly what you are experiencing. Maybe you've tried to build your own tool to address these needs, but the amount of coding and integration work is overwhelming. Did you know that there is a tool out there that can help you run all your queries from cache?
I. Background of the launch of Redis Data Integration (RDI)
Enterprises are faced with a large number of applications, a growing user base, expanding technology requirements, and a constant quest for real-time response.Redis Enterprise provides real-time access to data and can scale horizontally, but how do I align the Redis cache with the database so that all queries can be executed from the cache?
Some organizations decide to take it on themselves, only to find it very difficult to construct a cache preflight (or sometimes called an early refresh). They need to build a reliable streaming pipeline themselves. The first step is to capture all the data changes that have occurred in the source database and then convert the data to a Redis data type to allow applications to access it. This process usually involves data conversion and de-normalization. They require the integration of multiple components (Change Data Capture (CDC), streaming, and Redis connectors), code conversion, error handling, and many other enterprise basics, and the time spent on tool building can be spent doing more productive work.
In the face of all the problems faced by users of The much-anticipated public preview of Redis Data Integration (RDI) is now available, allowing developers to move databases to Redis Enterprise, mirror application data, and run at the speed of memory with no coding or integration effort.
II. Entering Redis Data Integration
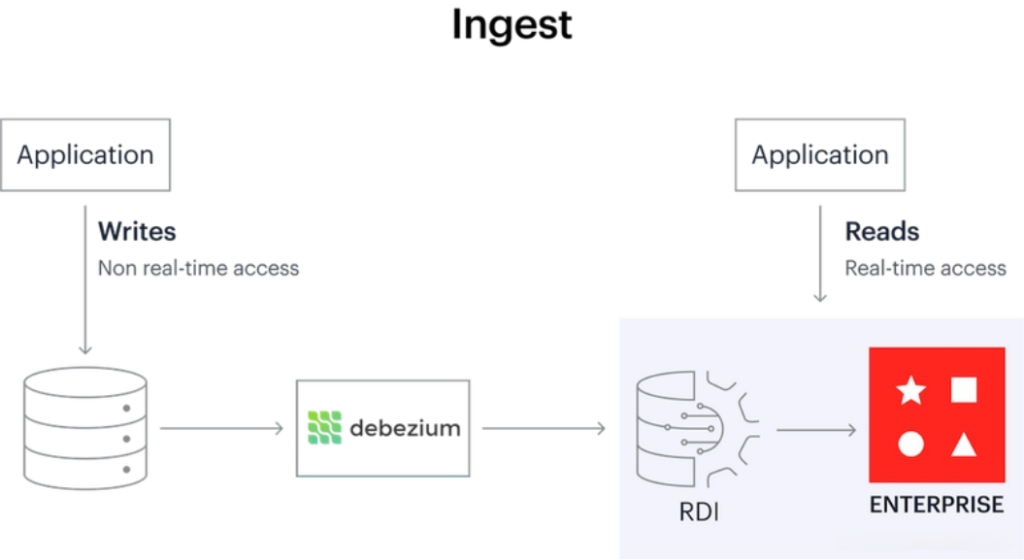
Redis Data Integration (RDI) is a tool that runs within Redis Enterprise. It helps users synchronize data from their existing relational database to Redis nearly instantaneously, so that application read queries are moved entirely from the relational database to Redis.
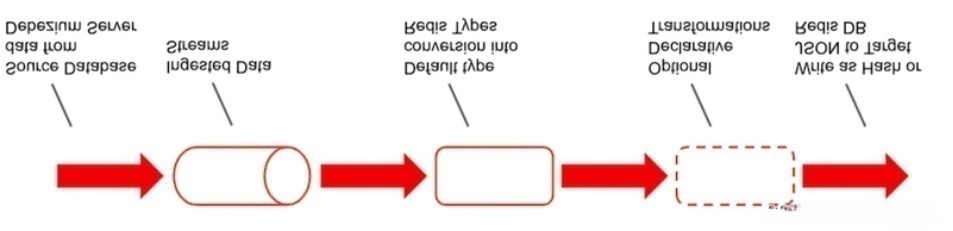
The RDI pipeline has two phases:
• Captures database changes and streams them to the RDI conversion task.
• Transforms and denormalizes the data using declarative commands, then writes it to the target Redis cache
Data conversion process:
• Debezium is an open source CDC platform that captures changes to data in the source database and streams them to RDI where the data can be further filtered, transformed, and mapped to one or more Redis keys.RDI supports a variety of Redis data types (Hash, JSON, Set, and Stream).RDI writes data to the target RDI writes data to the target Redis database. It takes care of the heavy lifting so developers can focus on application code instead of integration chores and data conversion code.
• RDI can connect to other CDC tools and data streams. With such an integrated solution, developers can use RDI as the core to stream changes from various databases to Redis Enterprise and other data platforms in a simple way.
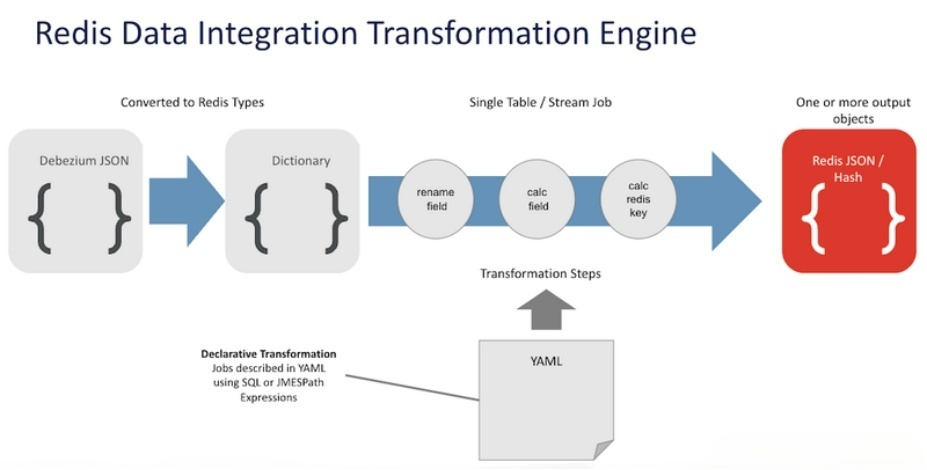
Code-free Data Filtering and Conversion
Capturing changes from the source database and transferring data from one place to another is hard enough. However, there is another challenge with mobile data: the transformation part, which means filtering the data and mapping it to the Redis data model.
1) RDI provides an option to specify all the filtering and transformation steps required for each source table. In RDI terminology, this is called a job; each job is a YAML file.
Filtering:
RDI does not require coding to perform filtering without requiring developers to write custom code. Developers can use declarative filters using SQL operations or Jmespath functions, and RDI comes with additional custom Jmespath functions for the convenience of job creators.
RDI has several levels of data conversion:
• Basic Conversion: This is done automatically by the RDI engine.
• Structured: The RDI engine has a default structure that can be constructed as a hash or JSON through the code-free conversion feature. You can choose to convert keys and fields and even recalculate the values in these fields.
• De-normalization: RDI converts the source data into a JSON document where the parent details in the document are converted into a mapping of JSON objects.
Troubleshooting:
RDI includes a traceability tool that helps developers create and troubleshoot complex data pipelines without writing custom code. This speeds up the process and reduces the amount of effort and skill required. After troubleshooting, the pipeline can be modified with a simple deploy command without downtime.
IV. Additional Features in the Open Preview Version
• Guarantee at least one delivery
• Debezium Server and RDI High Availability
• Hard Reject Entry Handling in Dead Letter Queue (DLQ)
• Supported source databases: Oracle, Postgres, MySQL, MariaDB, Percona XtraDB, Microsoft SQL Server and Cassandra (including DataStax DSE)
• Data extraction modes: initial snapshot and CDC (stream change)
• Declarative transformations: filtering conditions, Redis key patterns, changing field names, adding fields, deleting fields, nesting
• Supported Redis Data Types: Hash, JSON, Set, Stream
• Developer Tools: RDI Command Line Interface Scaffolding and Tracking Commands
• Operator tools: RDI command line interface, Grafana dashboard (pointer via Prometheus exporter)
When can I use RDI?
• The application data comes from a relational database and is not interchangeable.
• The relational database can accommodate the speed of data writes, but cannot be extended and executed to meet the load of read queries. Migration of read queries from the relational database is necessary.
• It is critical that the data in the cache reflect the data in the relational database in near real time.
• The change rate of the relationship database is medium-high, and batch insertion of changes does not satisfy the requirement.
• Data mapping between the source database and Redis requires some data manipulation.
Redis Data Integration (RDI) Development
The current version of RDI is a public preview, and the ability to integrate Redis in the opposite direction is being investigated: applying changes to Redis data to downstream databases.
• Write-behind: The CDC source is the user's Redis database and the user's target is the downstream relationship database or NoSQL database. This process will allow users to enjoy the real-time write and read speed of Redis Enterprise while preserving the application ecosystem and downstream services.
• Write-through: Each write to Redis is also applied to the relational database.
• Read-through: If a cache miss occurs, RDI automatically retrieves the missing data from the downstream database and writes it back to Redis as a key to return it to the requesting application.
How to start using RDI?
RDI is currently only available for self-managed Redis Enterprise clusters.
• If you are an existing Redis Enterprise customer, download the RDI CLI software package and follow the steps in the Quick Start Guide. The installation guide walks you through the installation and configuration of the Debezium server. After running some RDI CLI commands, your pipeline transfers data from the source database to Redis.
• If you are not an existing Redis Enterprise customer, you will need to first install the Redis Enterprise Software for Kubernetes, then download the RDI CLI software package and follow the steps in the Quick Start Guide.
If you are interested in the above content, please feel free toContact Us!