summaries
This article introduces Spring AI.Supporting databases are key storage technologies in LLM-driven applicationsPreviously, Spring had few options for launching AI applications built with Redis, and the Spring community is working on a Spring AI project to simplify development. The Search Augmented Generation (RAG) technology combines data and AI models, using the beer dataset as an example.Describes how loading data into Redis implements the RAG workflow.The code is available on GitHub and relies on Spring Boot, Azure OpenAI, etc. It also introduces the classes responsible for data loading, RAG processes, packaging HTTP endpoints, and the React interface to interact with Spring endpoints, making it easier for Java developers to build AI applications.

Introduction to Spring AI
In Large Language Model (LLM)-driven applications, the provision of databases often serves as the core storage technology for Artificial Intelligence applications. Such databases need to support semantic search and provide the relevant contextual environment for LLM.
Until now, the options for building AI applications with Spring and Redis were relatively limited. Recently, Redis has attracted a lot of attention as a high-performance supporting database solution. The Spring community has launched a new project called Spring AI, which aims to streamline the development process for artificial intelligence applications, especially those involving supporting databases.
The following section describes how to build a Spring AI application that implements a search augmentation generation (RAG) workflow using Redis as the backing database.
Search Enhanced Generation
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) is a technical approach that combines data with artificial intelligence models.In a RAG workflow, data is first loaded into a supporting database (e.g. Redis). Upon receiving a user query, the supporting database will retrieve a set of documents that are similar to the query. These documents are used as the context for answering the user's question and are combined with the user's query to generate a response, usually through an artificial intelligence model.
In this example, we will demonstrate this using a dataset containing information about various types of beers, with attributes such as the name of the beer, the alcohol content (ABV), the International Bitterness Units (IBU), and the description.The dataset will be loaded into Redis to demonstrate a practical application of the RAG workflow.
Codes and Dependencies
It can be found on GitHubSpring AI and RedisAll the code for the demo.
This project uses Spring Boot as a startup dependency for web applications, and combines Azure OpenAI and Spring AI Redis.
Data Loading
Our application will use JSON files that provide beer information as a data source. The structure of each file is as follows:
“id”: “00gkb9”.,
“name”: “Smoked Porter Ale”.,
“description”: “The Porter Pounder Smoked Porter is a dark rich flavored ale that is made with 5 malts that include smoked and chocolate roasted malts. It has coffee and mocha notes that create a long finish that ends clean with the use of just a bit of dry hopping ”,
“abv”: 8.,
“ibu”: 36
}
To load the beer dataset into Redis, we will use the RagDataLoader class. This class contains a method that runs when the application starts. In this method, we use a JsonReader to parse the dataset and then insert the file into Redis using an automatically connected VectorStore.
At this point, we have obtained a dataset of about 22,000 beers and their corresponding embeddings.
RAG Services
The RagService category implements the RAG workflow. When prompted by the user, it calls the retrieval method and performs the following steps:
- Management of calculation of user prompts
- Query the Redis database to retrieve the most relevant documents.
- Creating alert messages using file and user alert searches
- Use prompts to call the chat client to generate a response
SearchRequest request = SearchRequest.query(message).withTopK(topK);
// Query Redis for the top K documents most relevant to the input message
List docs = store.similaritySearch(request);
Message systemMessage = getSystemMessage(docs);
UserMessage userMessage = new UserMessage(message);
// Assemble the complete prompt using a template
Prompt prompt = new Prompt(List.of(systemMessage, userMessage));
// Call the autowired chat client with the prompt
ChatResponse response = client.call(prompt);
return response.getResult();
}
controllers
Now that we have implemented the RAG service, we can encapsulate it in an HTTP endpoint.
The RagController class exposes the service as a POST endpoint:
@ResponseBody
public Message chatMessage(@PathVariable(“chatId”) String chatId, @RequestBody Prompt prompt) {
// Extract the user prompt from the body and pass it to the autowired RagService
Generation generation = ragService.retrieve(prompt.getPrompt());
// Reply with the generated message
return Message.of(generation.getOutput().getContent());
}
user interface
On the user interface side, a simple React front-end was created to allow users to ask questions about beer. The frontend interacts with Spring by sending HTTP requests to the /chat/{chatId} endpoint and displaying the responses.
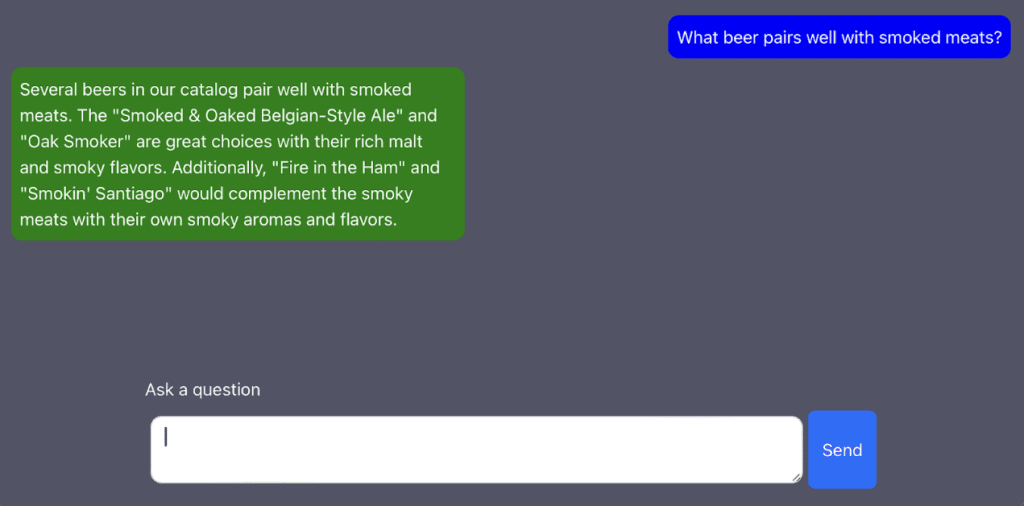
With just a few simple classes, we implemented a RAG application using Spring AI and Redis.
Next, we recommend that youView sample code on GithubCombining the efficiency and ease of use of Redis with the convenient abstractions provided by Spring AI will make it easier for Java developers to use Spring architectural response AI applications. By combining the efficiency and ease of use of Redis with the convenient abstractions provided by Spring AI, it becomes easier for Java developers to respond to AI applications using Spring constructs.
For more information about the support database, please feel free to contact us.
Learn more about our products

Redis Enterprise Cloud
● Real-time data, any scale, any deployment space
● Seamless data migration
:: True high availability
● Linear scalability and real-time performance
Redis Enterprise Database
● High-performance caching for business-critical applications
● Build local and cloud applications using modern data models
● Easily Migrate Local Data to the Cloud and Deploy Across Regions with Active-Active
If you are interested, you are welcome to follow us for more information about the article and contact us if you have any questions!