Semiconductor Silicon Intelligence, also known as IP core, is a hardware description language program with circuit-specific functionality, often used in digital circuits. The program is independent of the IC process and can be ported to different semiconductor processes to produce IC wafers, thus helping developers to reduce their workload and accelerate time-to-market.
1G Managed Redundant Switch IP Core- Available for Xilinx Vivado
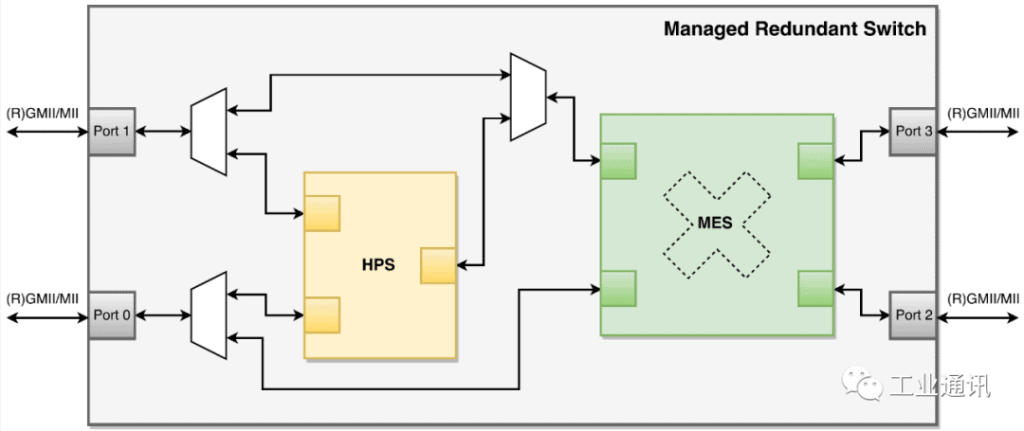
The Managed Redundant Switch IP core (MRS) is a combination of the Avision HSR-PRP Switch (HPS) and Managed Ethernet Switch (MES) IP cores with redundant Ethernet switching capabilities.The MES module is a non-blocking cross-switching matrix that allows continuous transmission between all ports. It implements a store-and-forward switching methodology to fully satisfy the Ethernet standard policy about verifying the integrity of each frame before forwarding it. On the other hand, the HPS module introduces HSR and PRP redundancy in the required ports. the switching method for HSR is Cut-Through. Therefore, the combination of MES and HPS provides the highest performance and maximum compatibility with the standard.
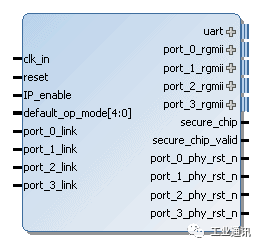
Managed redundant switches can be easily integrated into a user's FPGA design with the new Xilinx Vivado tool, which allows IP cores to be used and IP parameters to be configured in a simple way within the graphical user interface.
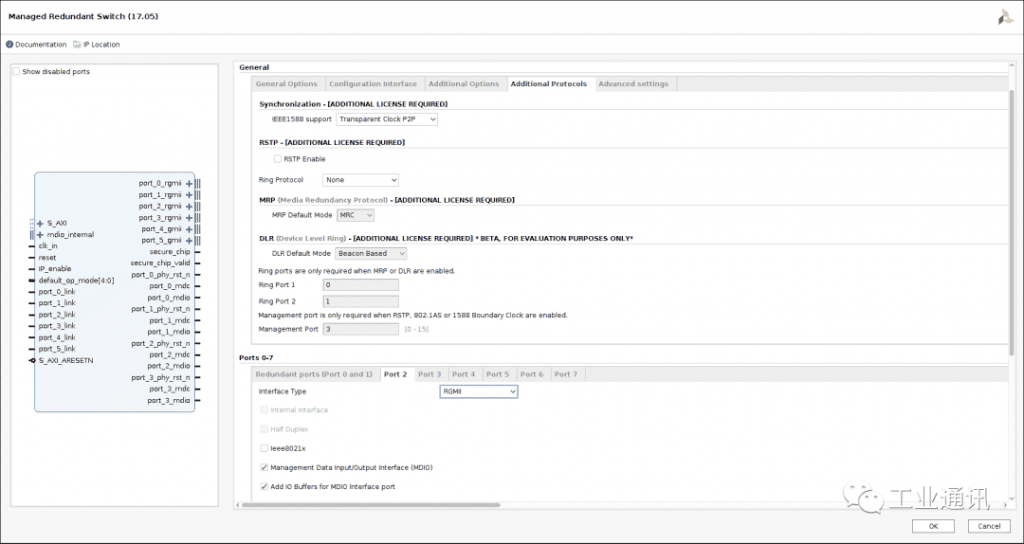
The following Xilinx FPGA families can support the Avision MRS IP core:
▪ 6 series (Spartan, Virtex)
▪ 7 series (Zynq, Spartan, Artix, Kintex, Virtex)
▪ Ultra-large (Kintex, Virtex)
▪ Ultrascale+ (Zynq MPSoC, Kintex, Virtex)
HK Network Management Redundant Switch IP Core Main Functions
# Interface
Full-duplex 10/100/1000 Mbps Ethernet interface
▪ Half-duplex 10/100 Mbps Ethernet interface
▪ Full-duplex 10 Gbps Ethernet interface (under development)
▪ Configurable 3 to 16 Ethernet ports
MII/ GMII/ RGMII/ SGMII/ QSGMII Physical Layer Device (PHY) interface
Each port supports different data rates.
▪ Copper and fiber media interfaces: 10/100/1000Base-T, 100Base-FX, 1000Base-X
# Exchange
▪ Dynamic MAC table with automatic MAC address learning and aging (up to 2048 entries)
▪ Static MAC table (up to 2048 entries)
▪ Giant frame management
Ethernet-based switching
▪ Entrance port mirroring
▪ Broadcast/multicast storm protection
▪ Rate limiting per port (broadcast, multicast and unicast traffic)
# Circulation management
Multicast frame filtering
▪ Translation port mask: user-defined frame to specific port forwarding
▪ Port-based VLAN support
▪ Quality of Service (QoS): priority (PCP-802.1p, DSCP TOS, Ethernet type)
▪ IEEE 802.1X EAPOL hardware processing
DSA (Distributed Switching Architecture) labeling: Ideally, Ethernet switches should support “switch labeling” when using DSAs.”
# Configuration
▪ MDIO, UART, AXI4-Lite or CoE (Configuration over Ethernet) management interface
Configuration over Ethernet (COE): full access to internal registers via the same Ethernet link to the CPU
▪ Provide drivers when purchasing IP cores
# Redundant agreements
▪ RSTP (requires software stack)
▪ MRP (no software stacks)
▪ DLR (no software stacks required)
▪ HSR (no software stacks required)
▪ PRP (no software stacks)