preamble
Active Directory (AD) Password PolicyPassword management is the key foundation for maintaining account security and identity authentication in enterprise security management. As organizations face certificate padding, brute force breaches, and increasingly stringent security compliance requirements, the need for an efficient approach to password management and continuous monitoring becomes even more critical. This article explains how to configure and optimize password policies in AD environments, and how toIncorporate the latest NIST guidelines與 Lepide Instant Audit ToolThe company's mission is to help organizations reduce the risk of account leakage and improve compliance, while taking into account user experience and operational efficiency.
The traditional "periodic password change" and "complexity mandatory rules" are no longer applicable. Depending on NIST SP 800-63B guide, companies are designing Account Security Policy In the case of a user-centered approach, a more effective approach should be adopted, for example:Passphrase.The system is designed to provide a comprehensive list of passwords, a filter of leaked passwords, and an intelligent password update mechanism.
Active Directory plays a central role in most enterprise IT organizations. Identity and Access Management System The Role. According to Lepide's AD Security Landscape Report, if organizations can implement strong password specification in account security management along with MFA Multi-Factor AuthenticationIn addition to significantly reducing the risk of account leakage, it can also effectively defend against attacks such as brute-force cracking and certificate stuffing. This article will further share how toCreating AD Coding Practices that Meet Modern Security StandardsIt helps organizations strike a balance between security, compliance and user experience.
How can I ensure that my Active Directory password policy is enforced effectively?
In a Windows domain environment.Active Directory (AD) Password PolicyIt is the core specification that determines how users create and manage passwords, and it is also the key foundation for corporate information security and compliance management. Key practices and best practices are organized below:
1. Mandatory password length
The current trend in information security no longer emphasizes "excessive complexity rules" or "mandatory periodic password changes," but rather recommends the use ofLong and Unique PassphraseAnd withLeaked Password List Filtering, to enhance the effectiveness of defense.
- According to the NIST SP 800-63B guide:A minimum of code 8 is acceptable but recommended.At least 12 yards or more。
- Passwords are supported up to 64 codes and allow spaces and Unicode characters.
This design minimizes the security risks associated with weak passwords while taking into account the user experience.
 Establishing a comprehensive AD encryption policy not only protects sensitive data, but also helps organizations meet security compliance requirements.
Establishing a comprehensive AD encryption policy not only protects sensitive data, but also helps organizations meet security compliance requirements.
2. Default Domain Policy
In Windows Active Directory, administrators can adjust the Default Domain Policy through the GPMC (Group Policy Management Console) to ensure that the settings meet the latest security standards and compliance requirements.
Suggested Settings:
Minimum 12 digit length: Ensures code strength and reduces the risk of weak codes.
Remove the complexity mandate: avoid users choosing hard-to-remember and insecure passwords in order to comply with the rules.
Enable Password History: Prevents users from reusing old passwords.
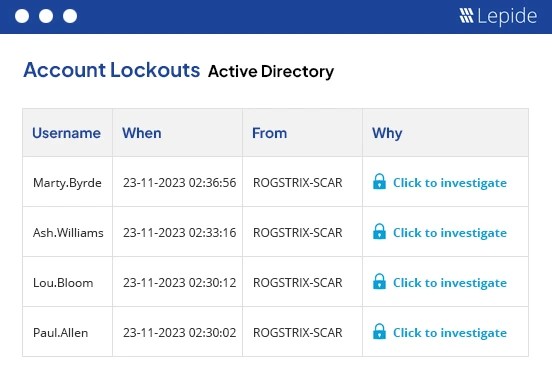
Account lockout strategy: e.g. 30-minute lockout after 10 failed login attempts, effectively blocking brute-force attacks.
This design not only enhances account security, but also improves the user experience, avoiding the inconvenience of the previous "mechanical complexity".
However, according to Lepide's Active Directory Security Landscape Report.Businesses with 43% often face account lockout problems.This has resulted in a surge in IT support work orders and business interruption. If you can optimize the default domain policy, you can effectively reduce the pressure of IT maintenance and improve the overall operational efficiency.
3. Apply Fine-Grained Password Policy (FGPP)
In Active Directory (AD).Fine-Grained Password Policy (FGPP) Different rules can be applied to different groups or accounts, especially for high-risk targets such as administrator accounts or service accounts. These accounts usually have higher privileges, and if compromised, the impact can be felt across the entire domain.
Practical advice:
Configuration: FGPP can be set up and managed through the AD Administration Center (ADAC) or PowerShell commands.
Context: ForPrivileged Accounts (Privileged Accounts) Stricter password length, complexity, and lockout rules are established, while the average user can maintain relatively loose settings.
Security Benefit: Separate high-risk accounts from general accounts to reduce overall security risk and make the strategy more flexible and practical.
👉 The flexible design of the FGPP allows organizations to develop corresponding AD password security policies for different roles, further enhancing security compliance and avoiding a one-size-fits-all approach that results in a poor user experience.
4. Code expiration strategy
In many businesses, theAccidental expiration of passwordThis often results in a large number of IT helpdesk work orders, causing user interruptions and decreased productivity.
Best Practices:
due date reminder: Automatically notifies the user a few days before the password is about to expire, avoiding unexpected lockouts.
Periodic Design: If corporate policy permits, it is recommended that the password expiration cycle be extended tofirst yearIt is not time-driven and is linked to actual risk events rather than purely time-driven.
Risk Determination: ForAccounts that have not changed their passwords for a long period of time are considered dormant or potentially high-risk accounts.In addition, we will further review the need for deactivation or enhanced control.
👉 These practices can play a key role in maintaining AD Password Security At the same time, theReduce IT maintenance stressIn addition, it will enhance the overall operational efficiency.
5. Ongoing maintenance and monitoring
Password policies alone are not enough to fully protect against Active Directory (AD) risks. EnterpriseMust be combined with continuous auditing and monitoringThe only way to ensure that the account and password policy is truly implemented is to make sure that the policy is implemented.
Proposed Measures:
Regular Checks and Optimizations: Regularly review your password policy for compliance with the latest security standards to avoid outdated or incorrect settings.
Service Account Management: in particularService Account PasswordIt should be replaced regularly and under strict control.
Automated Log Collection: Implement automated tools to collect and analyze AD logs for focused monitoring.Privilege upgrade, strategy change, abnormal login or lockout. and other events.
SIEM Integration: Integrate data into SIEM (Security Incident and Information Management System)The company conducts trend analysis, compliance verification and security risk alerts.
👉 Enhanced AD Coding StrategyIt can also identify potential threats in advance and reduce the incidence of information security incidents.
6. Multifactor Authentication (MFA) Enhancement
In the modern information security environment, passwords alone are no longer sufficient to secure your account.MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication) It should be regarded as a necessary measure in an enterprise's information security framework. By adding additional authentication elements, it will be difficult for an attacker to successfully log in to the system even if he has obtained a password.
Best Practice Recommendations:
Critical Accounts Must Be Imported: For accounts involving sensitive data, personally identifiable information (PII), or privileges.Proposed full activation of MFA。
Integration with SIEM: all cryptographic anomalies (e.g. brute force attempts, suspected certificate compromise)All should be directly connected to the SIEM system.collocationReal-time Alerts and Audit Functionsto ensure that the security team is able to respond in the first instance.
Enhance overall security maturity: MFA combined with an AD password policy can significantly reduce the risk of certificate padding and account intrusion, and at the same time, reduce the risk of certificate padding and account intrusion.Meet security compliance requirements (e.g. ISO 27001, GDPR)。
👉 AD password policy + MFA dual protection has become the basic configuration of enterprise information security, which can effectively reduce the operational impact of account leakage.
II. How to configure password policy in Active Directory?
在Active Directory (AD)In this environment, the password policy can mainly be used through theGroup Principle Management Console (GPMC)與Fine-Grained Password Policy (FGPP) The following table describes how to configure the settings.
Domain-wide standardization: If an organization wants to standardize the set of password rules across the domain, it can simply use the Default Domain Policy GPO。
Differential Demand: If there are different levels of account requirements in the organization (e.g., administrator accounts or privileged accounts), then the Windows Server 2008 and laterin which the use of FGPP Uniquely define password rules for specific users or groups.
Configuring the Default Domain Password Policy with GPMC
open up Group Principle Management Console (GPMC): Press Win + RInput
gpmc.mscand press Enter.Navigate to:Forest > Domains > Your Domain
在 Default Domain Policy Right-click → Edit
Path:Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Account Policies > Password Policy
After completing the changes, run the
gpupdate /forceLet the policy take effect immediately.
Common Domain Password Policy Settings
Enforce Password History: To prevent users from reusing old passwords.
Maximum Password Age: Set the maximum number of days that the password can be used, after which it must be replaced.
Minimum Password Age: The requirement that passwords can only be changed after at least a certain period of time prevents users from quickly and repeatedly changing them to bypass historical restrictions.
Minimum Password Length: It is recommended that at least 12 yards or more, to enhance security.
Complexity Requirements: Set whether passwords should contain case-sensitive letters, numbers, and special characters, and avoid using strings associated with user names.
Configure Fine-Grained Password Policy (FGPP, optional) for specific users/groups
If an organization needs to establish differentiated password rules for different groups or accounts.Fine-Grained Password Policy (FGPP) It is the best solution. This feature is especially suitable forAdministrator Account, Privilege Account 或 Service Account This effectively reduces the risk of a single account being compromised and spreading to the entire domain.
FGPP Setup Steps:
open up Active Directory Administration Center (ADAC)Enter System > Password Settings Container。
Right-click in a blank space and select "New > Password Settings"。
Define password and account lockout rules (e.g. minimum length, expiration time, limit on number of false logins, etc.).
在 Direct Applies To field to apply this policy to a specific user or Global Security Group (GSG)。
👉 Through FGPPWith a single Active Directory domain, organizations can configure dedicated AD password policies for different roles or groups, giving high-privileged accounts more stringent protection and general users a more flexible experience.
How Lepide Helps Protect Active Directory
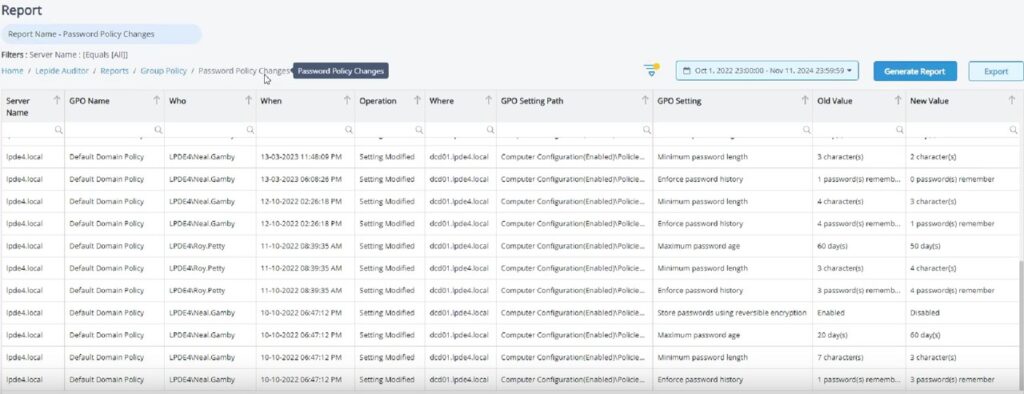
Compared to the Windows native tools that provide limited log and policy management.Lepide Active Directory Auditor In addition, it can provide more complete and real-time auditing capability to help enterprises to significantly improve the quality of their audits. AD Safety and Security Compliance Levels。
Lepide's core strengths:
Full tracking of changes: Complete capture of all Objects, Permissions, Login, Lockout, Group Principles The following is a list of the changes that have taken place, such as "who, when, where, and what".
Centralized Management ConsoleThe IT administrator can get real-time visibility from a single platform and target Key Events(e.g., password reset, account lockout, multiple login failures) sends real-time alerts.
Intelligent Alarm Mechanism: Support Threshold-based warning rulesIt automatically recognizes anomalous patterns and helps prevent brute-force cracking and certificate stuffing attacks.
Compliance Reports and Survey Tools: Built-in customizableCompliance report, logging history, lock-in cause analysisIt helps businesses to quickly troubleshoot problems and toCompliance with international security standards such as ISO 27001, GDPR, etc.。
Event Recall and Fast Recovery: When unnecessary or malicious changes are made, the administrator can roll back the settings immediately to minimize the impact.
👉 With Lepide, businesses can easilySimplify Active Directory Monitoring and Auditing ProcessesThe government is also able to take action at the first sign of a threat.EnsureAccount Safety, Information Security Compliance與Operational Sustainability。
Conclusion: Critical Measures for Account Security
An effective password policy is the cornerstone of protecting your organization's digital assets. However, password rules alone are not enough. The only way is to integrate the password policy with the overall security measures, and to carry outOngoing monitoring and auditingThe risk of account breaches and security incidents can only be minimized.
Proposed Measures:
- Distinguish between account types: Adopt differentiated password policies for privileged accounts and general user accounts to avoid high-privileged accounts becoming a single point of risk.
- Source Defense: Enhance password length, enable leaky password list filtering, and block weak password and certificate stuffing attacks.
- Import Passwordless Authentication: Gradually adopt modern password-less authentication technologies (e.g. FIDO2, Windows Hello, mobile device authentication) to reduce password dependency.
- Ongoing monitoring and auditing: Through AD auditing tools and SIEM systems, suspicious behavior can be detected and intercepted in real time, ensuring that security incidents can be stopped at an early stage.
👉 These measures effectively enhance Active Directory account protection while meeting corporate security compliance requirements, allowing IT teams to strike the optimal balance between security and user experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes. To avoid service interruption, it is recommended to set more flexible specifications for service accounts. System administrators can individually configure specific accounts through Group Policy (GPO) or Fine-Grained Password Policy (FGPP).
Yes. With FGPP, multiple sets of cryptographic rules can exist in the domain at the same time and can be applied to different objects as required.
Fine-Grained Password Policy (FGPP) allows different password specifications to be applied to different users or groups within the same domain, allowing for more granular management.
Check that the settings in the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) are applied correctly and that the policy is properly linked to the target group or account. Also, make sure that users are compliant with existing policies.
 in-depthLepide Active Directory Audit and Password Security SolutionsWhat?
in-depthLepide Active Directory Audit and Password Security SolutionsWhat?MAXTRIX provides a complete range of real-time audit tools and compliance reports to help organizations strengthen AD account protection and enhance security compliance.If you would like more informationFeel free to contact us now!Or schedule an appointment for a personalized consultation and we will be happy to assist you.
Honghong will provide you with any support you need!
Our professional Honghong team will be the first to respond and provide you with the best service to solve all your problems.



